C. FOULING:

Fouling is the deposition of suspended particles. The
particulate matter generally accumulates at low velocity areas in the cooling
water system. If cooling water is on the shell side of the heat exchanger then
because of low velocity the fouling material settles on the shell side.

Fouling is the deposition of suspended particles. The
particulate matter generally accumulates at low velocity areas in the cooling
water system. If cooling water is on the shell side of the heat exchanger then
because of low velocity the fouling material settles on the shell side.
Fouling Deposition:-
THE POTENTIAL FOULANTS IN COOLING WATER SYSTEMS ARE AS FOLLOWS:
- a) Dust and silt.
- b) Corrosion Products.
- c) Sand
- d) Natural organics
- e) Microbial matter
THE FOLLOWING FACTORS AFFECT THE FOULING OF THE SYSTEM:
- a) Water characteristics
- b) Temperature
- c) Water velocity
- d) Microbial growth
HOW DOES THE ANTIFOULANT WORK?
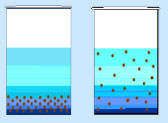
For fouling to take place, small suspended particles have to come together to
form Agglomerate. Most of the suspended matter is in the colloidal state and
have a small electric charge on them.
ANTIFOULANT is polymeric in nature and when it is
absorbed on suspended particles, it will increase the negative charge on the
particle. As like charges repel, the suspended particles are thus kept apart,
preventing their agglomeration. The particles thus stay dispersed in the water
and are prevented from depositing and fouling the system.
